Start with a powerful overview of the climate-energy nexus:
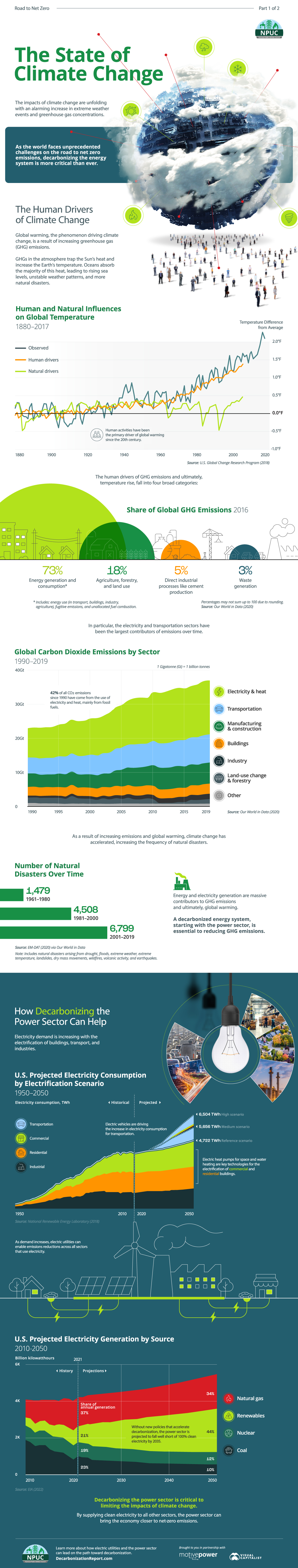
Climate change and energy systems are inseparable—fossil fuel dependence drives greenhouse gas emissions, while rising global temperatures intensify weather disasters that threaten both lives and infrastructure. Today’s story explores how fossil fuels continue to dominate, how renewables are scaling up, and why extreme weather events are reaching historic levels—from record-breaking heatwaves and wildfires to floods and cyclones. Through each section, expect fact-based analysis, visual storytelling, and real-world examples.
)
2. Fossil Fuels: The Backbone of Emissions
Dive into coal, oil, and gas:
- Current dependence: Fossil fuels still make up ~72% of global electricity generation climate.mit.edu.
- Carbon impact: Coal alone emitted nearly 14 billion metric tons CO₂ in 2020 solarnrg.ph.
- Who leads: China, the US, India, Saudi Arabia, and Russia dominate coal and oil emissions.
- Unequal effects: Vulnerable regions disproportionately bear health and infrastructure burdens from pollution and climate hazards .
3. The Rise of Renewables
Detail renewable energy’s growth and challenges:
- Growth stats: From 32 TWh in 2000 to 2,400 TWh in 2020, wind and solar now provide ~9% of global electricity developmentaid.org+12climate.mit.edu+12cbpp.org+12.
- Installed capacity 2025: Solar (~1,200 GW) and wind (~900 GW) power ahead technosustainability.com.
- Benefits: Zero emissions, job creation, distributed energy resilience.
- Barriers: Storage integration, grid upgrades, intermittent supply, capital costs, political resistance.

).
4. Climate-Driven Weather Extremes
Examine the surge in disasters:
Heatwaves:
- Southern Europe just saw 107–109 °F temps, “marine heatwave” ocean warmth, over 30% more heat-related deaths nca2023.globalchange.gov+10washingtonpost.com+10yaleclimateconnections.org+10.
- US heatwave in June 2025 broke records in 280 locations, 130 million under warnings, power system stress theguardian.com+1gbpsr.org+1.
- India–Pakistan heatwave: temps above 118 °F, ~260 fatalities. Pakistan hit hard—2005–2025 saw heath mortality surging among vulnerable groups en.wikipedia.org.
Flooding:
- San Antonio flash floods: 6.3 inches rain, 13 deaths, calls for smart infrastructure expressnews.com.
- South Africa floods in June 2025: 101 fatalities, $288 M damages en.wikipedia.org.
- Asia floods/storms: recent trend shows floods are leading causes of death—impacting India, Pakistan, Nepal public.wmo.int+1timesofindia.indiatimes.com+1.
5. Wildfires & Cyclones (~600 words)
Wildfire surge:
- California’s January 2025 wildfires driven by drought and wind patterns worsened by climate change .
- Global trend: 5 of 10 deadliest wildfires since 1900 have occurred since 2018; land-use and climate factors intertwined yaleclimateconnections.org+1capeweather.com+1.
Cyclone Alfred:
- Category 4 cyclone hit Queensland/New South Wales in early 2025, $820 M in damages en.wikipedia.org.
- Globally, insured losses from weather disasters projected at $145 B in 2025 weforum.org.
6. Feedback Loops: Why the Cycle Continues
Explain compounding effects:
- Fossil fuel emissions → global warming → more extreme weather → infrastructure & energy systems damage → increased resilience demand.
- Impacted energy infrastructure: supply, grids, pipelines, refineries nca2023.globalchange.gov.
- Health & economic tolls escalate—Pakistan’s children and elderly, $ billions in disaster costs globally .
7. Solutions & Forward Path
Mitigating emissions:
- Phase-out of coal, rapid solar/wind scaling, support for storage and hydrogen, carbon capture, modernization of grids.
- Policy levers: carbon pricing, subsidies rebalanced, emissions regulations, climate finance via COP30 theguardian.com.
Building resilience:
- Climate-smart infrastructure: flood controls, smart grids, heat-resilient buildings.
- Early warning systems (e.g., for avalanches in Himalayas) timesofindia.indiatimes.com.
- Emergency protocols: heatwave warnings, cooling centers, outdoor work endpoints.
Community and behavioral change:
- Individual actions: energy conservation, rooftop solar, electrified transport.
- Collective engagement: public support for green policies, social equity-driven approaches, labor protections in heat.
8. Case Studies
Europe 2025 Heatwave:
- Multi-country highs (42–43 °C), fire threats in Greece, banned outdoor work in Italy washingtonpost.comwashingtonpost.com+2theguardian.com+2apnews.com+2.
- Public measures: free pools, heat alerts.
India–Pakistan Heatwave:
- April–May crisis, 195–260 deaths, infrastructure strain, early wave season—warning of future extremes theguardian.com+1washingtonpost.com+1en.wikipedia.org.
South Africa Floods:
- June floods: 101 deaths, massive displacement, national disaster declared en.wikipedia.org.
9. Conclusion
Wrap up with momentum:
The intertwined relationship between energy systems, fossil fuel dependence, and climate-driven extremes highlights both risk and opportunity. Renewables offer a path forward, but require investment and resilience planning. As disasters rack up costs and human suffering, the urgency for action is undeniable. Daily Reports stands committed to delivering clear, data-driven coverage—stay tuned as we track the next developments on energy, climate policy, and the disasters shaping our world.
Next Steps for Publication
- Use high-resolution versions of suggested images.
- Add relevant captions explaining each figure.
- Consider adding pull-quotes or data highlights in sidebars.
- You could break the post into a multi-page series or add interactive charts for user engagement.
Related News on Climate Disasters & Energy·Policy
Extreme heat grips southern Europe as temperatures surpass 100 degrees
Severe heat waves hit Southern Europe as local authorities warn against wildfire risks
A call to San Antonio to ensure deadly flooding never happens again

‘Climate is our biggest war’, warns CEO of Cop30 ahead of UN summit in Brazil
Sources
Ask ChatGPT